- Home
- Mind & body
- Acute v chronic inflammation in the body: what’s the difference?
At CBHS we help you manage your health challenges. We believe in offering you the services, support and tools you need to live your best life.
Health and Wellness Programs are available to support eligible members towards a healthier lifestyle. Each Health and Wellness Program is subject to its own eligibility criteria.
Contact us for more information and to confirm your eligibility for a program.
Acute v chronic inflammation in the body: what’s the difference?
.tmb-articledet.jpg?Status=Master&Culture=en&sfvrsn=d5af43df_2)
Inflammation is part of your body’s immune response to harmful substances. In other words, infections, wounds,
and damage to any tissue would not be able to heal without an inflammatory response.
There are two types of inflammation: acute and chronic inflammation.
Acute inflammation
Acute inflammation comes on very quickly and usually resolves in two weeks or less. During this process, your body responds to harmful
substances, repairs damage to cells and carries away dead cells.
What are the symptoms of acute inflammation?
Some symptoms can include the following:
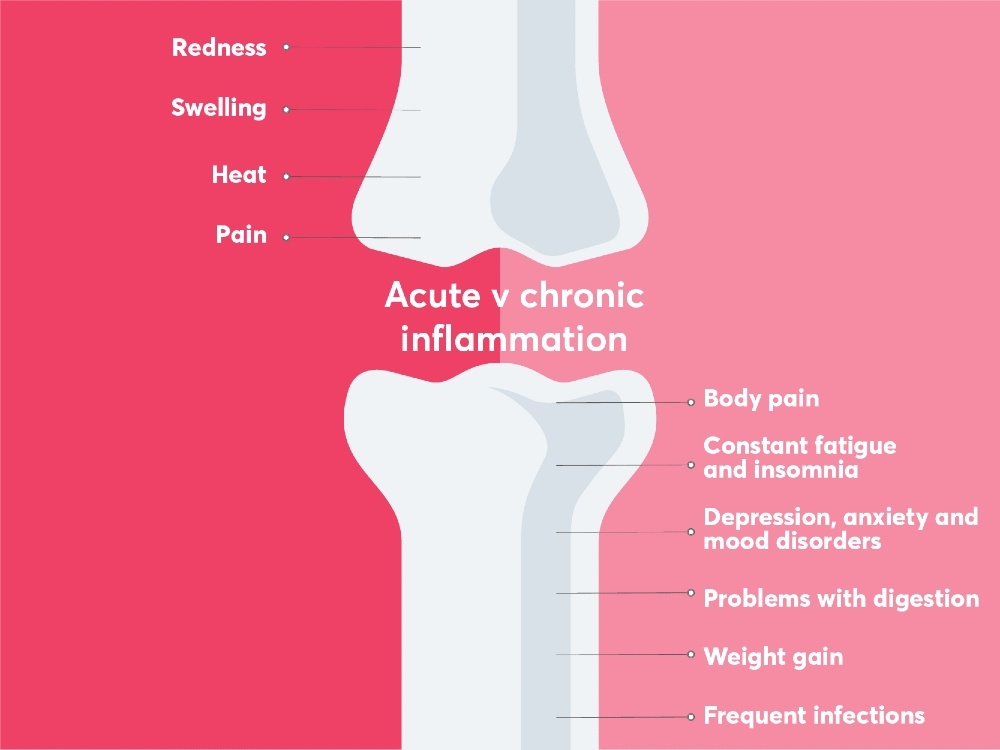
- redness
- swelling
- heat
- pain.
Examples of conditions that involve acute inflammation include acute bronchitis, a sore throat from a cold or flu or an infected ingrown toenail.
Chronic inflammation
Chronic inflammation is a slower and generally less severe form of inflammation. It can happen when your body can’t remove the harmful substance or heal an injury and this means your body stays in a state of inflammation for several months or even years. It can also happen if the harmful substance is gone but the body remains in an inflammatory state.
What are the symptoms of chronic inflammation?
Some symptoms can include the following:
- body pain
- constant fatigue and insomnia
- depression, anxiety and mood disorders
- problems with digestion
- weight gain
- frequent infections.
Research suggests there is a link between chronic inflammation and some chronic diseases. These chronic diseases include cardiovascular disease, chronic kidney disease, and type 2 diabetes.
“The symptoms of chronic inflammation can vary from body pain to constant fatigue, insomnia and infections.”
Inflammation v infection: what’s the difference?
An infection can cause an inflammation in your body. However, an infection is purely based on the growth of organisms. An inflammation is what happens when your body reacts to it.
There are five risk factors for chronic inflammation
- Obesity
There is a link between obesity and chronic inflammation. In fact, when someone is obese, their body is more likely to be in a state of inflammation. So, if you’re in this category, it’s a good idea to start looking at weight loss strategies. You can speak with your GP who may recommend you see a dietitian for tips on a successful weight loss plan.
- Diet
If your diet is high in saturated fat, trans fat, or refined sugar, you’re more likely to have higher levels of inflammatory markers in the body. However, if you have a diet that’s similar to a traditional Mediterranean diet, this can reduce the level of inflammatory markers in your body.
- Stress and sleep disorders
If you’re experiencing physical or emotional stress, you’re more likely to experience chronic inflammation in your body. Stress can also lead to sleep disorders and there is a link between irregular sleep patterns and an increase in inflammation in the body.
- Smoking
Smoking, or breathing in second-hand smoke, can also create chronic inflammation in your body. Often the immune system overcompensates for the intake of these toxins, which can mean that the white blood cells – rather than healing the damaged tissue – work on the offensive. This increases the risk of lung cancer.
- Age
The older you are, the more likely you are to experience chronic inflammation. This may be due to the increase of free radicals in your body as well as other age-related risk factors like an increase in visceral fat.
“A diet rich in fruit and vegetables, exercise and more rest and relaxation can help to fight inflammation in the body.”
What are some of the outcomes of chronic inflammation?
Over time, chronic inflammation can cause damage to healthy cells, organs and tissues. Eventually this can result in a breakdown in DNA, internal scarring and even tissue death. These can all lead to the development of many diseases.
The top six ways you can fight inflammation
- Eat your veggies and fruit
A diet rich in fruit and vegetables is one of the best ways to avoid chronic inflammation. Vegetables are full of anti-inflammatory nutrients, including magnesium, carotenoids, antioxidants and lycopene.
The following vegetables and fruits are particularly anti-inflammatory:
- tomatoes
- olive oil
- green leafy vegetables like spinach and kale
- fruits such as strawberries, blueberries.
- Limit these foods
The following foods have been found to increase inflammation in the body:
- refined carbohydrates like white bread and pastries
- fried foods
- soda
- red meat and processed meats
- margarine, shortening and lard.
- Eat more fatty fish
Foods rich in Omega-3 fatty acids can be anti-inflammatory. You can try adding fatty fish such as salmon, mackerel, tuna or sardines to your diet.
- Exercise regularly
Regardless of your weight, regular exercise can help prevent chronic inflammation and reduce your risk of chronic disease.
- Get more sleep
It’s important to make sure you’re getting enough sleep. If you’re not getting adequate sleep, you’re likely to be at a higher risk of inflammation. Read more about tips to getting a good night’s sleep
- Relax
People with anxiety or depression can lower their inflammation markers simply by getting treatment. Lowering stress of any kind is going to lower your risk of inflammation.
A change in diet and lifestyle can improve levels of chronic inflammation
You don’t have to try and cope with chronic symptoms of inflammation in silence. Like most health issues brought on by obesity, high stress levels, and an unhealthy diet and lifestyle, chronic inflammation can be treated.
For more information and guidance on how you can fight inflammation for a better quality of life, speak with your health professional.
All information contained in this article is intended for general information purposes only. The information provided should not be relied upon as medical advice and does not supersede or replace a consultation with a suitably qualified healthcare professional.
Sources:
New study reveals the key to weight loss success (cbhs.com.au)
How a dietitian can help you lose weight (cbhs.com.au)
Stress and your body (cbhs.com.au)
Sleep apnoea, sleep paralysis and other causes of sleep deprivation (cbhs.com.au)
How can a gratitude journal change your life? (cbhs.com.au)
Health and wellbeing
programs & support
You Belong to More with CBHS Hospital cover:
- Greater choice over your health options including who treats you
- Get care at home with Hospital Substitute Treatment program
- Free health and wellbeing programs to support your health challenges
Live your healthiest, happiest life with CBHS Extras cover:
- Benefits for proactive health checks e.g. bone density tests, eye screenings
- Keep up your care with telehealth and digital options
- Save on dental and optical with CBHS Choice Network providers


